The Revenue Model is one of the fundamental elements of a startup’s business plan. It is, in short, the plan through which the company expects to generate profit. You should know, right from the start, that a startup can adopt different types of revenue models. Precisely for this reason it’s important that you know exactly what a Revenue Model is: the exact definition, practical examples and useful advice you’ll find in this guide will help you.
What the Revenue Model is
Far too many entrepreneurs confuse the Revenue Model with the Business Model. Before delving into the main differences between these two models, it’s necessary to clarify first of all what the Revenue Model is.
Definition and meaning of Revenue Model
The definition of Revenue Model, as already mentioned, is linked to the strategy through which the company intends to generate profit and, thus, sustain its financial growth over time. In more practical terms, a revenue model illustrates the way in which the company can obtain money through the sale of its products or services but also through other activities, including interactions with its customers. To be even clearer, the Revenue Model describes the various revenue generation mechanisms and their relative sources.
Revenue Model vs Business Model: main differences
Although many use the terms Revenue Model and Business Model as interchangeable, they are not synonyms and, in fact, refer to distinct aspects. But what is a Business Model? And what differentiates it, therefore, from the Revenue Model we have just defined?
The concept of business model refers to the logic through which the company creates, distributes and collects value. The term Revenue Model, on the other hand, refers to the way in which revenue is generated from the value created for customers.
To be clearer, the Business Model is what defines the company’s strategies and operations and the management methods linked to them, while the Revenue Model, precisely based on the information just mentioned, outlines the way in which the company will earn money.
Business models, generally, are represented by using the Business Model Canvas, which contains within it the main elements of the Business Model, including the one relating to Revenue (income). The Revenue Model, therefore, is part of the Business Model.
Why defining a Revenue Model is essential
Good, now that you know what a Revenue Model is and that you know it’s not a synonym for Business Model, the time has come to understand why it’s essential to define one. There are essentially two reasons.
Economic and financial sustainability
The first reason why it’s essential to define a Revenue Model is linked to the economic and financial sustainability of the startup or company itself. Pay attention because very often this aspect is underestimated and becomes the reason for the company’s failure: without a well-defined and clear Revenue Model, in fact, the startup may encounter problems covering costs or expanding in the market.
If you don’t want your company to fail, take time and employ the right resources to carefully develop your revenue model, taking into consideration all the variables that could have an influence on your ability to secure revenue (in a sustainable way).
Attracting investors and stakeholders
The second reason is partially linked to what was said just now: a good pitch capable of attracting investors and stakeholders for the startup cannot disregard a careful analysis and evaluation of the way in which the startup itself plans to generate revenue. Taking for granted that the product or service will be sold, therefore, is certainly not enough. What’s needed is to specify how this will be done. Only in this way, in fact, can you manage to demonstrate the feasibility and sustainability of your business.
Types of Revenue Model
In the introduction to this guide we previewed that there are different types of Revenue Model. Let’s get to know them together.
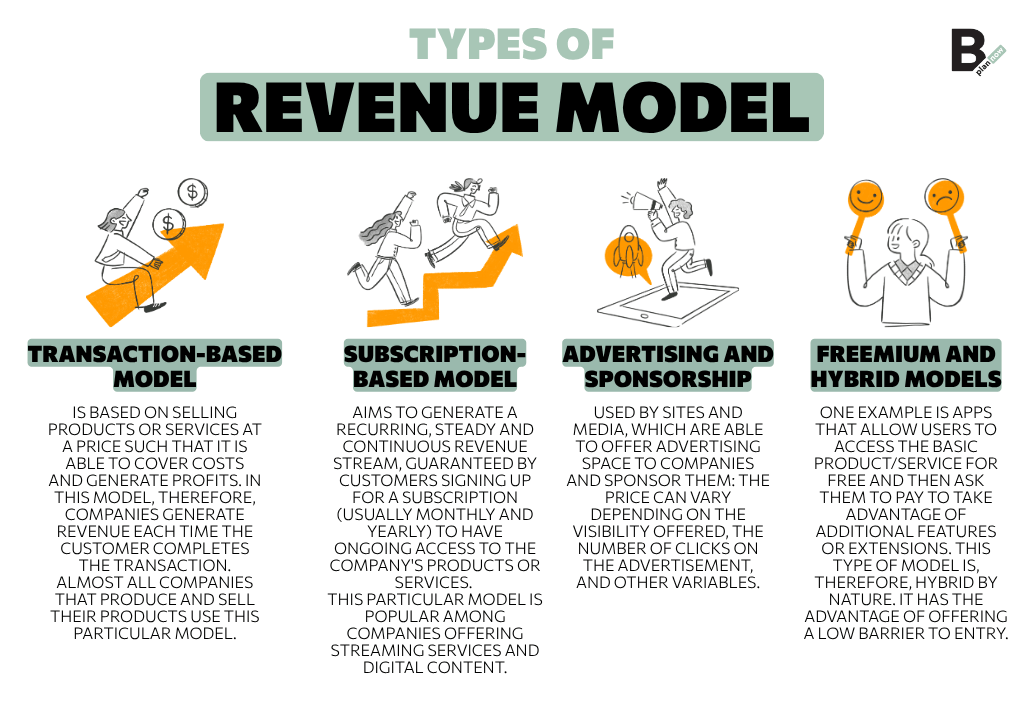
Model based on sales and transactions
The first type of revenue model is based on the sale of products or services at a price such that it’s able to cover costs and generate profits. In this model, therefore, companies generate revenue every time the customer completes the transaction.
Almost all companies that produce and sell their products resort to this particular model.
Subscription-based model
The Revenue Model based on subscription aims to generate a recurring, constant and continuous revenue stream, guaranteed by customers’ subscription to a subscription (generally monthly and annual) to have continuous access to the company’s products or services.
This particular model is very widespread among companies that offer streaming services and digital content.
Advertising and sponsorship
The Revenue Model based on advertising is generally used by sites and media, which are able to offer advertising space to companies and sponsor them: the price can vary based on the visibility offered, the number of clicks on the advertisement and other variables.
Freemium and hybrid models
There is another type of Revenue Model defined as freemium and hybrid. An example is represented by apps that allow users to access the basic product/service for free and then ask to pay to be able to use additional functions or extensions. This type of model is, therefore, hybrid by its nature. It has the advantage of offering a low barrier to entry.
How to create and write your Revenue Model
Let’s now move from theory to practice: you’re about to discover how to create and write your revenue model.

Analyzing the market and competitors
Before you start putting pen to paper, you must necessarily analyze the market and your competitors.
Market analysis, specifically, is useful for you to learn more about the socioeconomic context in which your startup operates, assess possible obstacles, and intuit opportunities for success and potential. Not only that, you need it to validate your business model and shape your business plan with a data-driven strategy.
Through competitive analysis, you can grasp the strengths and weaknesses of your rivals and define your unique value proposition that can secure your competitive advantage.
Identifying the most suitable revenue sources
The next step is to identify the best revenue sources for your business. As mentioned in the previous paragraph, there are many, from direct sales to subscriptions, passing through advertising spaces and collaborations with other companies. Choosing the right source (and, consequently, the right model) is essential to correctly meet the needs of the ideal customer and to therefore ensure the sustainability of your startup over time.
Modeling and testing the Revenue Model
The third and final phase of the process of creating and writing a Revenue Model is the one that involves its modeling and, then, its testing. Modeling means precisely defining the mechanisms through which the startup generates revenue. Once defined, the revenue model must be tested, so as to evaluate its actual effectiveness and validity. Remember, in this regard, the famous words of Peter Drucker:
“You can’t manage what you can’t measure“.
Revenue Model: concrete examples and case studies
We promised you in the introduction to this guide a list of concrete examples and case studies of Revenue Models that have become famous.
Netflix and the subscription model
The first example concerns Netflix and its model of revenues generated by subscriptions, which offer access to the wide catalog of movies, TV series and other shows in exchange for payment of a fee. This continuous and substantially stable and predictable revenue stream has allowed the company to invest massively in the creation of new content capable of building loyalty among already “engaged” users and attracting new customers.
Google and the advertising-based model
Another typical example is that of Google and its advertising-based revenue model. The main source of income for the search engine is, in fact, online advertising, paid by advertisers who want to acquire a visibility space within the search engine itself, on Youtube and the other platforms of the group. To this are added other sources, such as hardware sales (for example Pixel smartphones) or Youtube subscriptions.
Practical advice for effective Revenue Modeling
Before concluding this guide we want to give you some more practical advice for effectively building the revenue model for your startup. Let’s start with the mistakes you absolutely must avoid.
Common mistakes to avoid
The main mistake to avoid regarding Revenue Model, as already mentioned, is to underestimate its importance. Navigating by sight, in the belief (or, worse, in the hope) that revenues will arrive in one way or another is not contemplated.
The other common mistake is to proceed with creating the revenue model without taking into consideration the context in which the company operates, that is, more specifically, without preliminarily proceeding with the analysis of the market and competition.
Useful tools and resources for revenue modeling
Connecting to what was just said, it’s impossible not to mention SWOT analysis among the useful resources for effectively building a Revenue Model. Another useful tool is the already mentioned Business Model Canvas, of which revenues represent an entry. In this regard, you should know that B-PLANNOW®, in consideration of the fact that the canvases in circulation are now considered obsolete (if not outdated), has created THE B−PLANNOW BOARD®, a shared visual language composed of 23 elements to create the business model of your startup.
Do you want to read all the articles related to the stage your startup is in?