The Business to Consumer (B2C) business model involves companies selling their products or services directly to consumers. If you want to get to know it better, you’re in the right place: in this guide, you’ll find a complete definition of this model, the winning strategies to put into practice (with practical examples), the advantages and opportunities to seize, as well as the challenges to face.
Definition of the B2C model
The meaning of Business to Consumer (B2C) refers to the sale of products or services by a company directly to end consumers for their personal use. This business model underpins many of the daily transactions we all carry out—at supermarkets and brick-and-mortar retail stores (for example, a shop selling clothing), in service businesses (like restaurants or hair salons), but also on e-commerce websites and apps.
How direct-to-consumer sales work
Direct-to-consumer sales, as structured in the Business to Consumer model, make the purchasing process shorter and simpler because they eliminate intermediaries. Not only that: without reseller markups or agent commissions, companies adopting the B2C model can apply lower prices to their products or services, benefiting consumers.
Winning B2C marketing strategies
The term B2C also applies to communication methods between companies and end consumers, as well as to the marketing strategies typical of this business model. Unsurprisingly, selling directly to private customers requires specific techniques, different from those needed to sell to other businesses. Here are the most effective ones.
Emotion-driven content marketing
B2C content marketing should focus on how the product or service is used and the emotional and/or social benefits that come from purchasing it. Common examples include how-to guides, FAQs, and product comparisons with prices and reviews. Keep in mind that using testimonials—people (famous or not) who have purchased the product or service and can attest to its quality and effectiveness—reinforces other customers’ purchasing decisions.
Social media and direct interaction with the audience
Social media marketing is another powerful ally at your disposal. On these platforms, you can interact directly with your target audience (that is, end consumers), collect feedback, and quickly respond to doubts and requests. To engage consumers and encourage purchases, you can use storytelling and sensory stimulation through impactful photos and videos. Remember Seth Godin’s words:
“People don’t buy goods and services. They buy relations, stories, and magic.”
Personalized email marketing
Email marketing strategies are also valuable tools, but—to be effective—you must personalize your communications and enrich them with engaging images and videos. Many companies with a B2C business model use newsletters to keep customers updated on product or service news and upcoming events.
User experience and customer journey in e-commerce sites
E-commerce websites are true online storefronts for companies selling through the Business to Consumer model. If you want your site to positively impact sales, pay particular attention to the user experience and the customer journey: optimize pages for mobile, make content easy to browse, and ensure smooth navigation.
Advantages of the B2C model for startups and SMEs
As promised in the introduction, let’s examine the advantages the B2C business model offers companies—especially startups and SMEs. The main benefits are three.
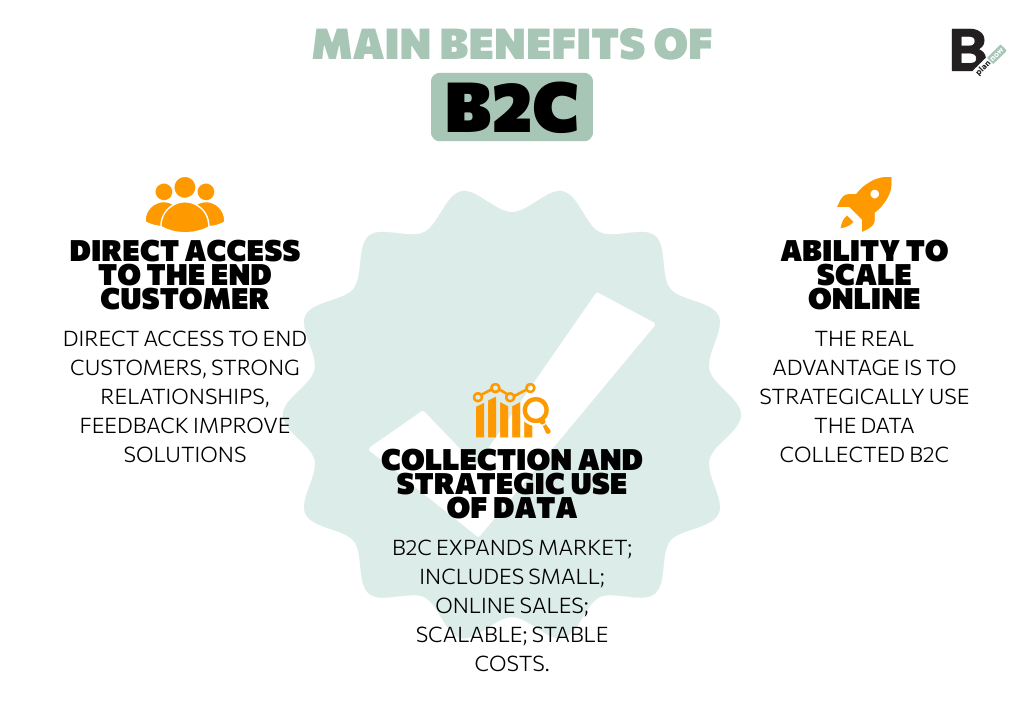
Direct access to the end customer
The first advantage is the ability for startups and SMEs to access their end customers directly. This interaction enables building stronger, longer-lasting customer relationships and improving products or services based on valuable feedback from consumers.
Scalability online
A Business to Consumer model provides access to a wide consumer market not only for companies already operating nationally or internationally but also for small local businesses, thanks to the opportunity to sell online. It is also a scalable model, as it allows companies to increase customers without costs rising proportionally.
Strategic data collection and usage
Another key advantage of the B2C model is the ability to collect valuable consumer data through direct relationships between company and customer. The real difference, however, lies in the ability to use this data strategically, from consumer behavior patterns to conversion statistics.
The main challenges of B2C
Like most things in life, there’s always a flip side: beyond the benefits of the B2C model, you must also be aware of the challenges. Here are the three main ones.
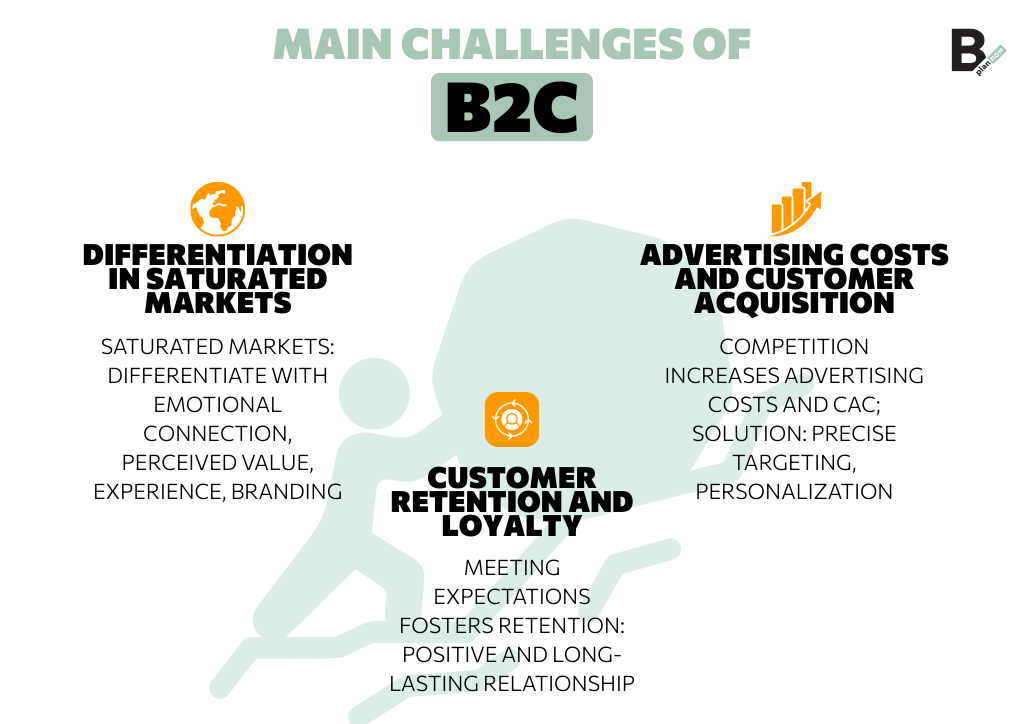
Differentiation in saturated markets
The first challenge is finding ways to stand out from competitors in saturated markets. The key lies in creating an emotional connection with customers, focusing on perceived value, enhancing the customer experience, and strengthening branding.
Advertising costs and customer acquisition
Intensifying competition in B2C markets, along with factors such as the increasing complexity of online marketing, can drive up advertising and customer acquisition costs. The “secret” to overcoming this challenge is to precisely identify your target audience, so you can optimize campaigns and deliver personalized solutions and experiences.
Customer retention and loyalty
Meeting the precise expectations and needs of your customers is what allows you to address the third challenge in Business to Consumer markets: Customer Retention and loyalty. The goal is to build positive, long-term relationships with your customers.
Differences between B2B and B2C
To fully understand the B2C business model, it’s important to highlight how it differs from B2B (Business to Business).
Target audience and purchase motivations
The first difference lies in the target audience and the reasons for purchase. A B2B company serves other businesses, while a B2C company targets private end customers. The latter purchase products or services to satisfy personal needs, while businesses do so to improve operational efficiency or generate a return on investment.
Length and complexity of the decision-making process
B2B and B2C also differ in the duration and complexity of the decision-making process. In the B2C model, the purchase decision is usually made by one person (the consumer), often based on emotions. In contrast, the B2B model involves a longer and more complex process, as it includes multiple stakeholders and is driven by data and detailed information about the product or service.
Examples of B2B vs. B2C businesses
Comparing B2B and B2C businesses helps highlight the differences. B2C companies sell directly to consumers, such as supermarkets, neighborhood shops, restaurants, hair salons, streaming platforms like Netflix, and e-commerce sites like Amazon.
B2B organizations, on the other hand, sell products or services to other companies. Examples include producing components for the automotive industry or selling enterprise software solutions.
Examples of successful B2C strategies
Let’s now look at some standout examples of B2C strategies that have proven successful.
DTC brands that revolutionized the market
One of the most cited examples of successful DTC (Direct-to-Consumer) brands is Warby Parker, the eyewear company founded in 2010. It pioneered online virtual try-ons and revolutionized the market with its Home Try-On service, which lets customers select up to five frames, have them delivered, and try them at home for free.
Another example is Velasca, a Milan-based startup in the footwear industry. Its competitive edge lies in producing the same high-end shoes in the same factories as major brands but selling them at much lower prices by bypassing wholesalers, distributors, and resellers.
How online communities support B2C marketing
Online communities play a powerful role in B2C marketing. The ability for companies to directly engage with groups built around users’ shared interests and activities increases sales opportunities. Pinterest is a clear example, allowing companies to promote products through sponsored pins aimed at interested consumers.
Subscriptions and membership models
Another successful strategy is the use of subscriptions and membership-based models. Streaming platforms are prime examples: in exchange for a monthly fee, they provide access to extensive catalogs of video and/or audio content.
The future of B2C and opportunities for startups
Before concluding this guide to the B2C business model, let’s examine emerging trends and the opportunities ahead for startups.
Emerging trends: e-commerce, mobile first, and artificial intelligence
E-commerce, which allows companies to reach customers anytime without third-party involvement, will continue to play a decisive role for businesses operating under the B2C model.
According to research by the Osservatorio eCommerce B2C Netcomm – School of Management at Politecnico di Milano, the product-based B2C e-commerce market will keep growing in 2025 (+€2.1 billion compared to 2024), moving from +5% in 2024 to +6% in 2025. Globally, Statista data suggests that B2C e-commerce sales will reach $8 trillion by 2026.
Other emerging trends in Business to Consumer include a mobile-first approach and artificial intelligence, which enhances efficiency (by optimizing operations and decision-making) and customer experience (through better personalization).
How to adapt your business model to changing consumers
Given these Business to Consumer (B2C) trends—and more—you should know there’s only one way to adapt your business model to new consumer needs and habits: understand them promptly, regularly analyze their behaviors, and always maintain a proactive, flexible mindset.
Do you want to read all the articles related to the stage your startup is in?